Coding experts tend to use 30-40% of their time only for comprehending the already existing code. These are two entire working days every week that are wasted on going through obsolete documentation, understanding ambiguous code, and desperately searching for developers who quit months ago.
On the November 2025, Google presented a remedy: Code Wiki, an artificial intelligence-based tool that provides documentation for whole code repositories that are always up to date. This is not merely a new documentation tool; it is a complete overhaul of the way we perceive the understanding of codebases.
What is Google Code Wiki?
Code Wiki is an innovative documentation system that always syncs your code documents to your real codebase. Unlike conventional documentation that gets outdated rapidly, Code Wiki, with the help of AI, surveys repositories, composes detailed wikis and all of it gets updated automatically after every commit.
Try to picture that, there is an expert developer who knows your whole codebase, is always ready and instantly carries out the updates for all documentation whenever the code changes.
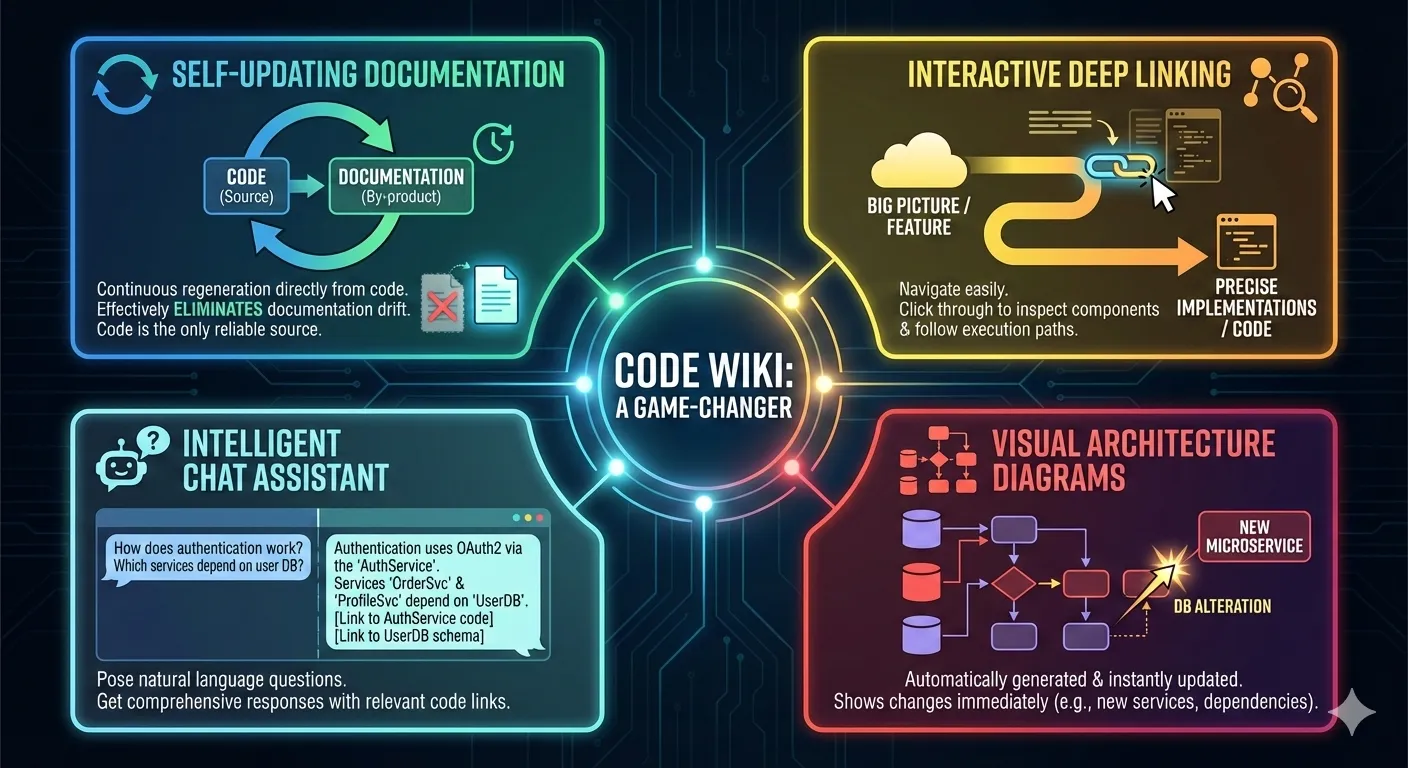
Key Features That Make Code Wiki a Game-Changer
Here are some of the standout features of Code Wiki:
- Self-Updating Documentation: The Code Wiki considers documentation to be a by-product, with the code being the only reliable source. The regeneration of documentation is a continuous process that effectively eliminates the problem of documentation drift, which is a major issue.
- Interactive Deep Linking: You can now navigate easily between the big picture and the precise implementations. While reading about a feature, you may see the code, inspect the related components, and follow the execution paths by clicking through.
- Visual Architecture Diagrams: Diagrams that are automatically generated will be updated when changes are made to your code. Have you created a new microservice or altered a database dependency? The architecture diagram will show this immediately.
- Intelligent Chat Assistant: You can pose questions in natural language such as “How does authentication work?” or “Which services depend on the user database?” and receive comprehensive responses along with links to the relevant code parts.
Deployment Options for Code Wiki
- Public Preview: Open-source repositories can be submitted to the Code Wiki site for auto documentation that is publicly viewable.
- Gemini CLI Extension: Corporate groups have the option to run Code Wiki on their own servers for confidential repositories (waitlist access).
Hands-On 1: Explore Code Wiki with Open Source
Step 1: Visit the Code Wiki public preview and search for a familiar repository (LangChain, LangGraph, etc.)
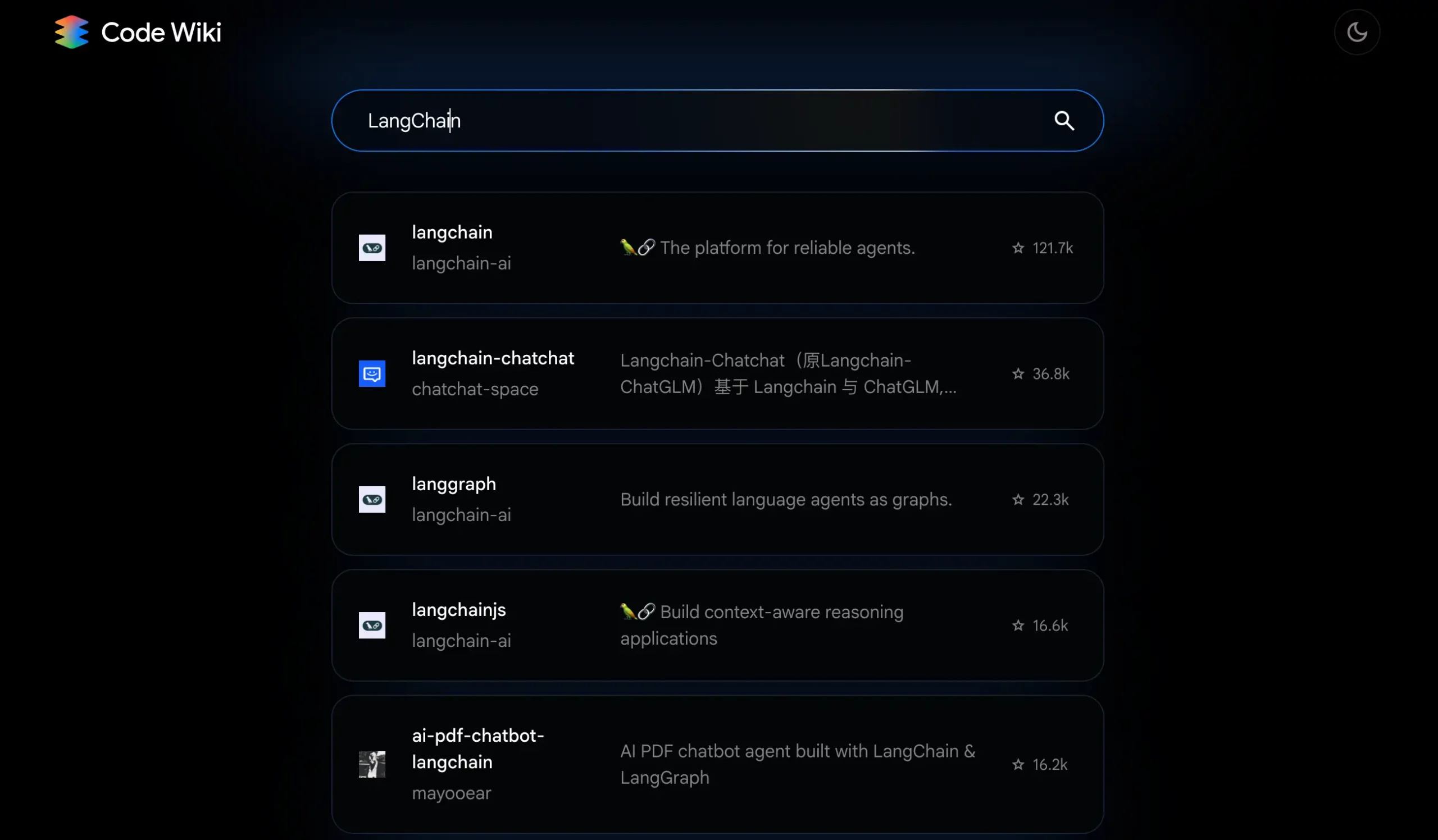
Step 2: Navigate to the repository overview. Identify major modules, dependencies, and entry points.

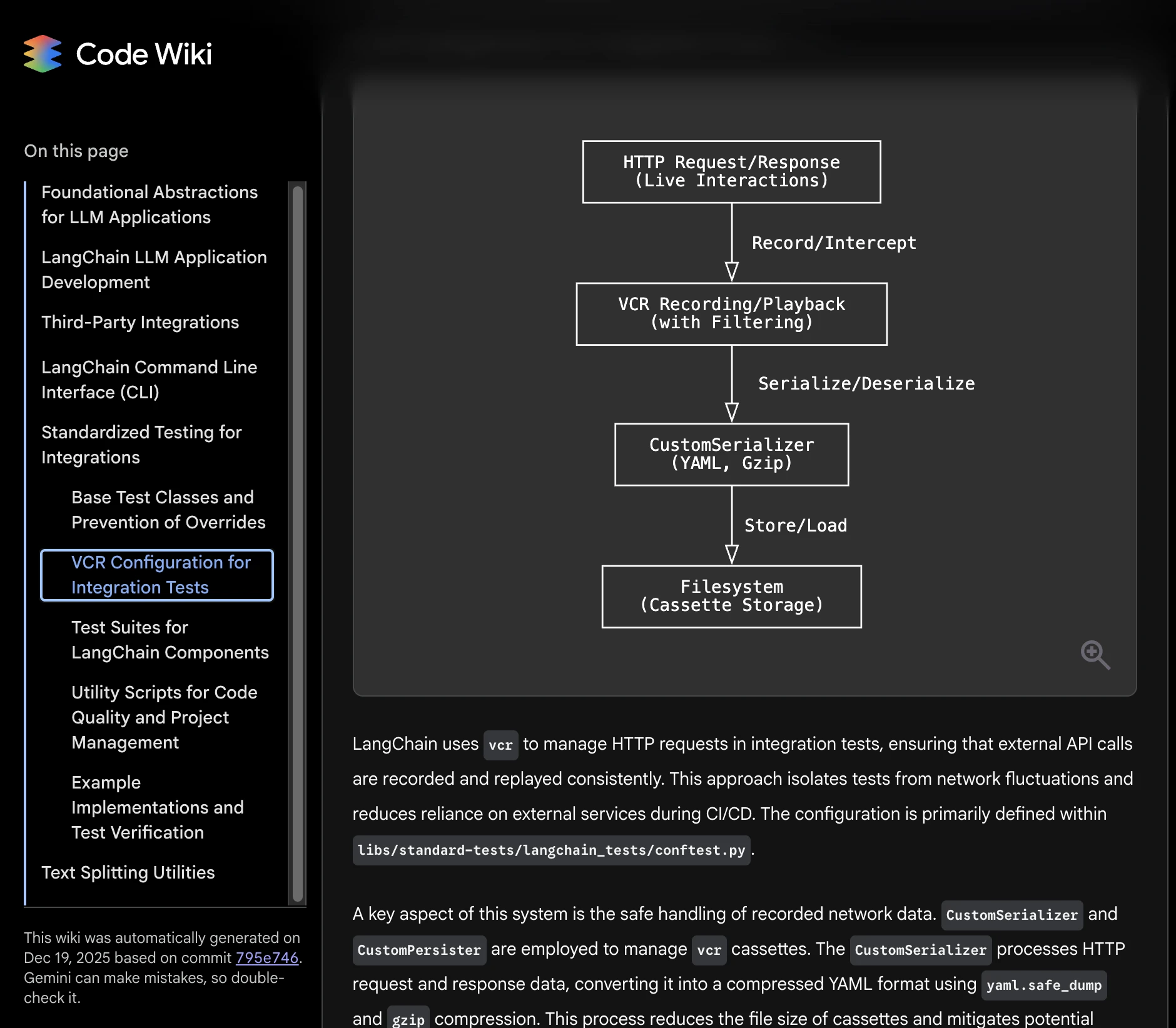
Step 3: Deep dive into a specific feature. Follow documentation from high-level description to implementation, clicking through code links.
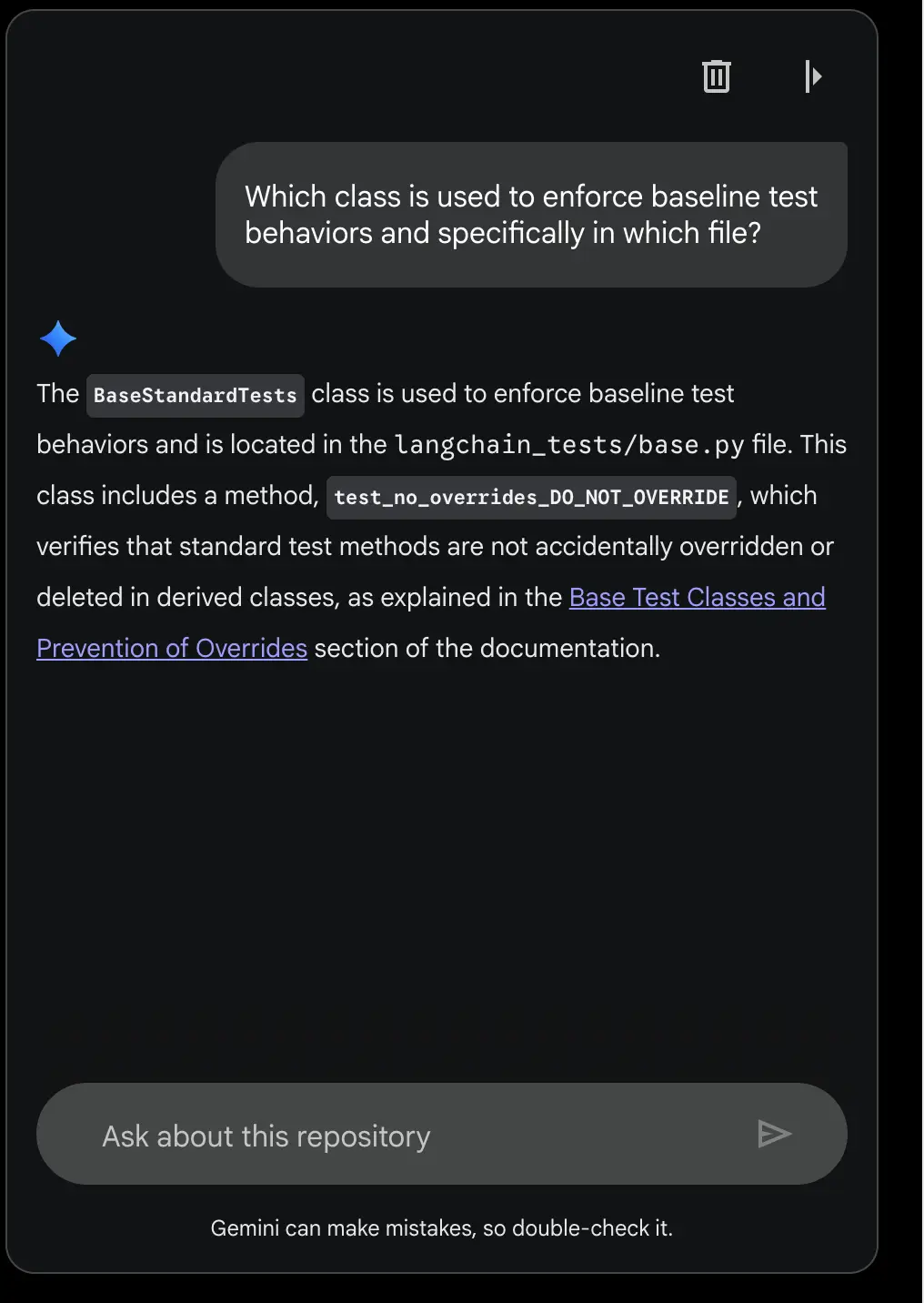
Step 4: Use the chat interface. Ask: “What design patterns are used?” or “How is error handling implemented?”
Step 5: Compare the project’s official docs. Notice differences in freshness, navigation ease, and connection between concepts and code.
Hands-On 2: Exploring Visual Relationships
1. Go to the public preview of Code Wiki.
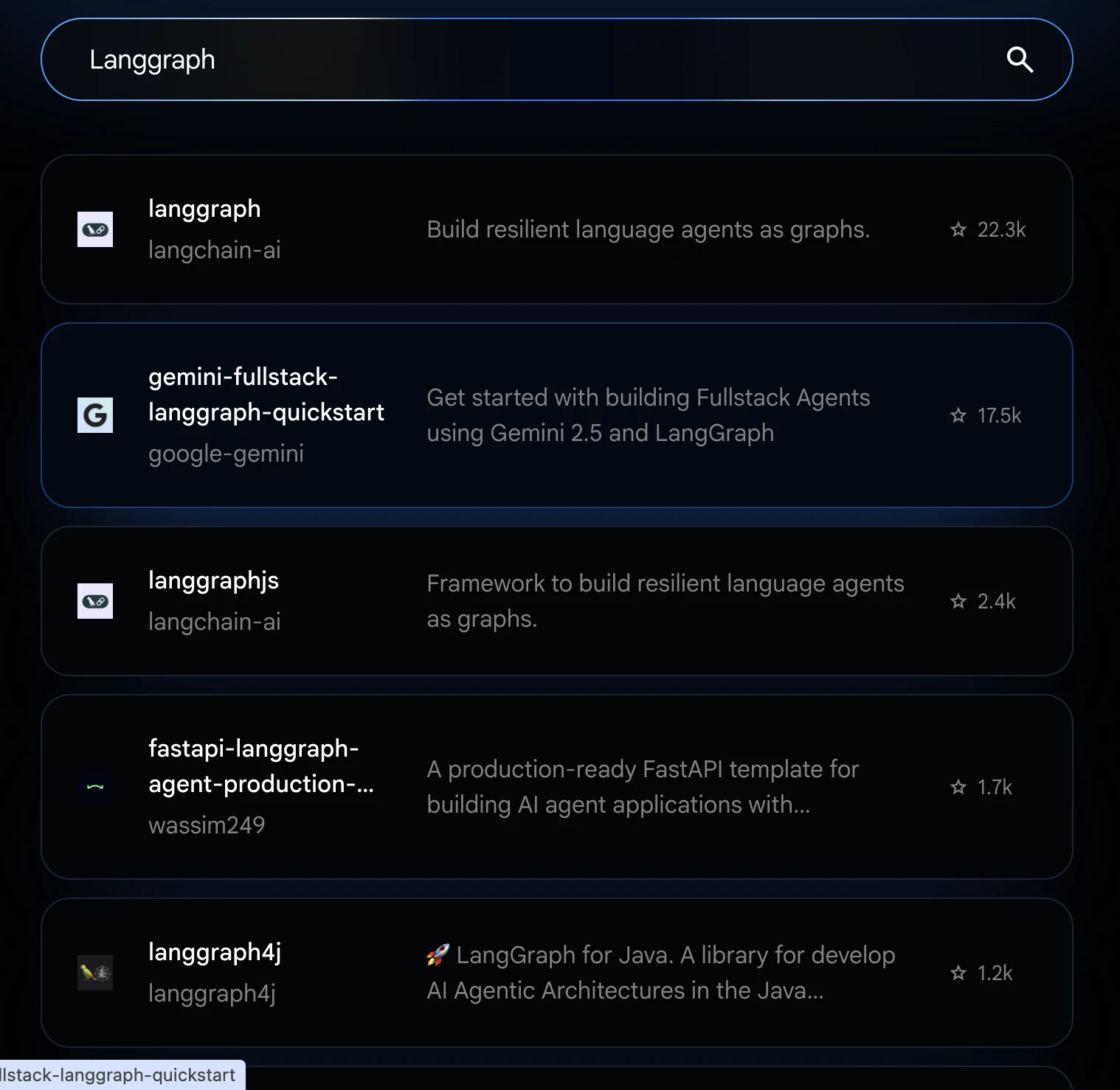
2. Enter your preferred repository name and choose the one you want to go for from the list.
3. After selection, you’ll see a sidebar having all the code part divided into different sections.
4. Prompt the model to depict a visual relationship, or you can use the following prompt
“Make a diagram depicting the entire workflow of this repository.”
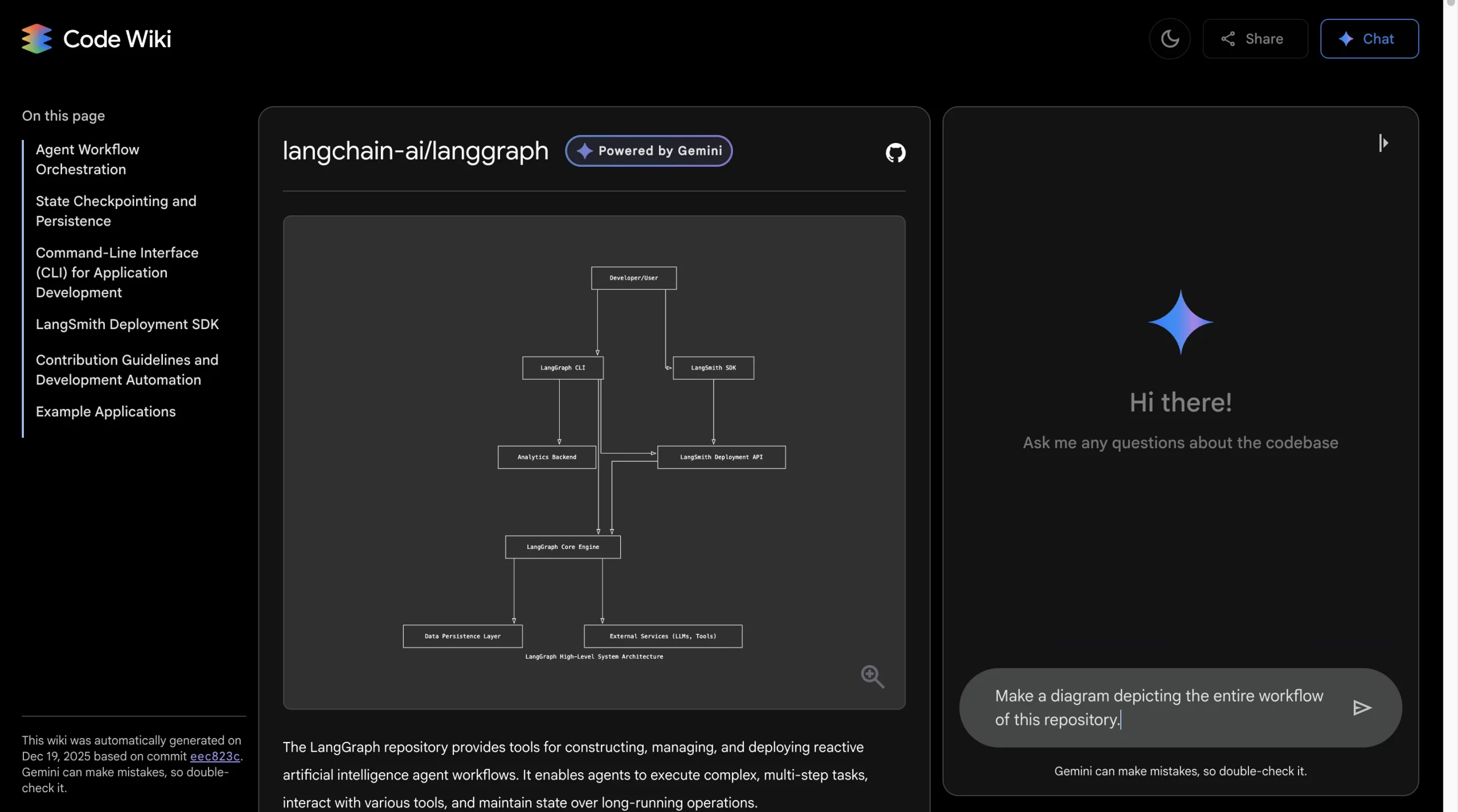
Output:
Code Wiki vs. Traditional Documentation
| Traditional Docs | Code Wiki |
| Manual creation | Automatic generation |
| Quickly outdated | Continuously updated |
| Disconnected from code | Directly linked |
| Time-consuming maintenance | No manual maintenance |
| Often incomplete | Comprehensive coverage |
Important Note: Code Wiki is a powerful tool for human documentation. It is the perfect one for “what” and “how” while human documents still cover “why” and the business context.
Real-World Applications of Code Wiki
The real-word applications of Code Wiki are:
- Accelerating Onboarding: New developers receive instant assistance for frequently asked questions, navigate the systems on their own and make a significant contribution in a few days rather than weeks.
- Legacy System Understanding: Examine old codebases where developers have already left, creating huge documentation for making changes easier.
- Cross-Team Collaboration: Groups can gain access to the documentation of other services, realize the points of integration and find out the dependencies without holding meetings all the time.
- Open-Source Accessibility: Lower significantly the entry limit for contributors by offering complete and always updated documentation.
Limitations of Code Wiki
With all that Code Wiki has on offer, there are a few downsides too:
- Context Gap: Code is documented but not the reasoning behind the architectural decisions
- Domain Knowledge: Knows the programming patterns but might have difficulties with the business concepts particular to the domain
- Quality Dependency: Good structure of the code leads to good documentation
- Coverage: The support is for the most popular languages and frameworks only
Conclusion
Google Code Wiki tackles one of the biggest challenges in software development: the discrepancy between what the code does and what the developers understand. With continuously updated, AI-based documentation, it guarantees faster learning, less frustration, and the spending of more time in building rather than in deciphering.
As Code Wiki progresses towards more extensive access, it will influence our coding structure, team collaboration, and new developer onboarding. The documentation revolution has started; AI is the force behind it.
Frequently Asked Question
A. It tackles the massive time drain caused by outdated or missing documentation by automatically generating and updating docs directly from the codebase after every commit.
A. Traditional documentation is written manually and quickly goes stale. Code Wiki uses AI to stay in sync with the code, offers deep links to implementations, generates live architecture diagrams, and lets developers ask natural language questions about the code.
A. While it explains what the code does and how it works, it does not capture the why behind architectural decisions, depends heavily on code quality, and currently supports only popular languages and frameworks.
Login to continue reading and enjoy expert-curated content.

